Pathophysiology of the Effects of Alcohol Abuse on the Endocrine System
Search
Epigenetic Effects of Ethanol on the Liver and Gastrointestinal System
Epigenetic modifications are emerging as important dynamic mechanisms contributing to both transient and sustained changes in gene expression. In some cases, epigenetic changes even can be inherited, although the mechanism for this remains elusive. Several types of epigenetic modifications have been studied in recent years. For example, several laboratories have actively examined modifications, of...
Epigenetic Control of Gene Expression in the Alcoholic Brain
Whether a specific gene is transcribed or repressed is determined by the specific status (i.e., conformational state) of the complex of chromosomal DNA and proteins (i.e., the chromatin) and by the recruitment of specific proteins (i.e., transcription factors) to regulatory sites on the DNA (Copeland et al. 2010). Chromatin states can change as a result of enzyme-mediated covalent modifications of...
Alcohol's Effect on Host Defense
Alcohol has been the most common substance of use and abuse in human history. Moderate amounts of alcohol are enjoyed for its anxiolytic effects; however, its addictive properties can lead to chronic, excessive alcohol use and alcohol use disorder. In addition to its commonly recognized behavioral effects, alcohol affects many organs, including the immune system that controls the body’s defense...
Impact of Alcohol Abuse on the Adaptive Immune System
In the United States, alcohol use disorder (AUD) is the third-leading cause of preventable death. It is associated with increased susceptibility to bacterial pneumonia; viral infections, such as HIV and hepatitis C virus (HCV); and increased postoperative morbidity and mortality. This increased susceptibility is mediated in part by functional alterations in various cells of the immune system. The...
Women and Alcohol - From the Editors
Recent epidemiological research has identified alarming trends in drinking patterns of girls and women in the United States. In recent years, the amount and frequency of alcohol use are increasing in White and Hispanic girls and young women in contrast to decreasing patterns of heavy alcohol use in boys and young men.1,2 Similarly, current and binge alcohol use is rising among older women,3,4 resu...
NIH’s Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study (ABCD Study)
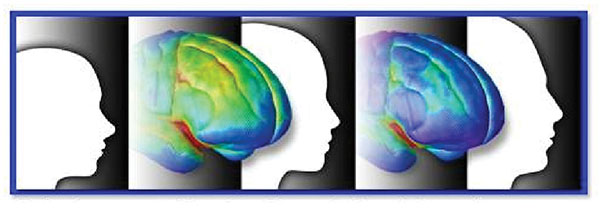
Adolescence is the stage of life during which most people begin using alcohol, and it is also a time of considerable social, psychological, and physiological change. The brain, particularly the frontal cortex, continues to develop throughout adolescence and does not fully mature until early adulthood. Adolescent alcohol exposure can impair brain development, compromise short- and long-term...
The Role of Innate Immunity in Alcoholic Liver Disease
Heavy consumption of alcohol poses a well-known health risk worldwide. Alcohol’s effects on health and well-being are numerous and include injuries and fatalities resulting from alcohol-induced incapacitation. Moreover, chronic and heavy alcohol consumption affects the integrity and function of vital tissues and organs, causing slow but significant structural and functional damage over time. One...
Recovery in Special Emphasis Populations

